Background
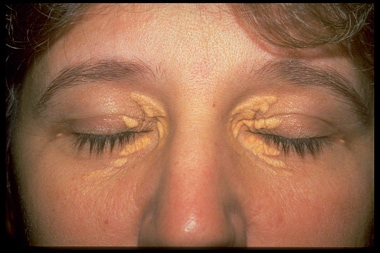
Xanthelasma are yellowish plaques that occur most commonly near the inner canthus of the eyelid, more often on the upper lid than the lower lid. Xanthelasma palpebrarum is the most common cutaneous xanthoma.
Xanthelasma can be soft, semisolid, or calcareous. Frequently, they are symmetrical, and all four lids are sometimes involved. Xanthelasma tends to progress, coalesce, and become permanent.
The term xanthelasma is derived from the Greek xanthos (yellow) and elasma (beaten metal plate).
See Can You Recognize Benign Skin Lesions From Cancerous Ones?, a Critical Images slideshow, to help identify various skin lesions.
Pathophysiology
Xanthelasma are a type of xanthoma appearing on the eyelids. Xanthomas are depositions of yellowish cholesterol-rich material that can appear anywhere in the body in various disease states. They are cutaneous manifestations of lipidosis in which lipids accumulate in foam cells within the skin. They are often associated with hyperlipidemias, of both primary and secondary types. Some occur with altered lipoprotein composition or structure, such as lowered high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. They frequently occur in patients with type II hyperlipidemia and in the type IV phenotype.
Epidemiology
Frequency
United States
Xanthelasma are not uncommon.
International
In India, the incidence of xanthelasma may range from 0.3%-1.5%. [1]
Mortality/Morbidity
These lesions have no premalignant potential; however, see Differentials.
A study by Christoffersen et al finds that xanthelasmata can be a predictor of risk for myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, severe atherosclerosis, and death in the general population, independent of well-known cardiovascular risk factors (eg, plasma cholesterol, triglyceride concentrations). On the other hand, arcus senilis of the cornea has been found not to be an important independent predictor of risk. [2]
Sex
In case studies of patients with xanthomatosis, a predominance of xanthelasma in women has been seen; women, 32%, and men, 17.4%.
Age
The age of onset ranges from 15-73 years, with a peak in the fourth and fifth decades.
Prognosis
Recurrence is common. Patients need to be aware that studies completed after surgical excision showed recurrence in up to 40% of patients. This percentage is higher with secondary excisions. Of these failures, 26% occurred within the first year and were more likely to occur in patients with hyperlipidemia syndromes and in those with all 4 eyelids affected.
Patient Education
For excellent patient education resources, see eMedicineHealth's Cholesterol Center. Also, visit eMedicineHealth's patient education articles High Cholesterol, Cholesterol Charts, Lifestyle Cholesterol Management, and Cholesterol Lowering Medications.
-
Case presentation of excision of recurrent xanthelasma. Recurrent xanthelasma bilateral upper lids; previous excision combined with blepharoplasty; patient insistent on repeat excision and blepharoplasty; advised of lagophthalmos risk due to medial position and lack of medial dermatochalasis.
-
Close-up view of recurrent xanthelasma right upper lid. Note the scar from previous excision by a plastic surgeon. Careful examination reveals subtle infiltration in the lateral aspect of scar.
-
Xanthelasma. External view, 1 week after surgery. Sliding and rotational flaps from residual lateral dermatochalasis used for medial excisional gap.
-
Xanthelasma. Top image, 4 weeks after surgery; lower image, before surgery.
-
Xanthelesma of four eyelids in patient with hyperlipidemia.