Practice Essentials
Globe retraction may result from neurogenic, myogenic, or mechanical etiologies.
Co-contraction of extraocular muscles due to synkinesis or aberrant firing can lead to retraction on a congenital or acquired basis.
Scirrhous breast carcinoma can produce enophthalmos.
Trauma is the most common cause of acquired enophthalmos.
The silent sinus syndrome can also present with enophthalmos.
Background
Globe retraction occurs when the globe is displaced deeper within the orbit from its normal position.
There are many causes of globe retraction. It may result from active co-contraction of the horizontal rectus muscles such as in Duane retraction syndrome. Patients with Duane syndrome have strabismus, upshooting or downshooting eye movements, narrowing of palpebral fissure, and retraction of the globe on adduction. [1, 2] Enlargement of the orbital cavity after orbital blowout fractures from trauma also may cause the globe to be retracted. [3, 4, 5] This may result from prolapse of orbital contents into the adjacent paranasal sinuses, atrophy of orbital fat, or contracture of necrotic extraocular muscles entrapped within the fracture. Globe retraction also can be seen in metastatic scirrhous breast carcinoma from cicatrization of orbital tissue. [6, 7, 8, 9] Although less common, some cases of the sclerosing variant of idiopathic orbital inflammation (pseudotumor) have been reported to cause globe retraction. [10, 11]
A thorough history and examination are required to determine appropriate management for patients with globe retraction.
Pathophysiology
Mechanism for globe retraction in Duane retraction syndrome is believed to be anomalous innervation of lateral rectus muscles from branches of oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve III). [2] Both electromyographic and autopsy studies in Duane syndrome patients have demonstrated this anomalous innervation. In attempted adduction, simultaneous contractions of lateral and medial rectus muscles cause the globe to retract. [12] Anomalous innervation between medial rectus and vertical rectus or oblique muscles also may explain upshoots and downshoots seen in adduction.
Traumatic blowout fractures typically occur when a large blunt object strikes eyelids and globe. The impact of the force causes retropulsion of orbital contents with an increase in intraorbital pressure. This results in fracture of the orbital floor and/or the medial wall. [3] Blowout fracture along with compression of air in the paranasal sinuses partially absorbs force of impact and prevents rupture of globe. Globe retraction results from either enlargement of orbital cavity after blowout fracture or prolapse of orbital tissue into adjacent sinus. Orbital fat atrophy or contraction of an entrapped extraocular muscle also can cause globe retraction after orbital blowout fractures.
Incidence of globe retraction in metastatic orbital tumors has been reported to be 10-25%. [13] Most common orbital metastasis to cause globe retraction is scirrhous breast carcinoma (82%), although it also has been reported with lung, gastrointestinal, and prostate carcinomas. The cause of globe retraction is cicatrization with contraction of myofibroblasts in orbital tissue. [7]
A similar mechanism can cause globe retraction in sclerosing idiopathic orbital inflammation (pseudotumor). Immunohistologically, sclerosing orbital pseudotumor resembles idiopathic retroperitoneal and idiopathic mediastinal fibrosis; several authors have suggested common pathophysiology. [10, 11]
Epidemiology
Frequency
United States
In the general population, prevalence of Duane retraction syndrome is 0.1%. [1, 2] It accounts for approximately 1% of all strabismus cases. Commonly, left eye more often is involved in Duane syndrome (OS:OD is 3:1); 20% of cases are bilateral. [14]
Eye injuries account for approximately 100,000 visits to physicians annually. In the National Basketball Association (NBA) eye injury study, eye injuries accounted for 5.4% of all injuries and included orbital fractures. Orbital fractures commonly result from motor vehicle accidents, interpersonal violence, and sports-related injuries. Baseball, basketball, ice hockey, and racquet sports are considered high-risk sports. [3, 4]
Metastatic tumors of the orbit account for approximately 1-13% of all orbital masses. [7, 13] Metastasis of breast carcinoma to the orbit accounts for approximately 50% of orbital metastases. Prostate and lung carcinoma follow in frequency accounting for approximately 17% and 6%, respectively.
Mortality/Morbidity
Duane retraction syndrome: Incidence of amblyopia is similar to that in the general population. Binocularity often can be maintained with abnormal head position. Indications for intervention include cosmetically unacceptable strabismus in primary gaze, anomalous head position, retraction of globe, or large upshoot/downshoot eye movements. Duane syndrome has been reported to be associated with some systemic anomalies, including Goldenhar syndrome, Klippel-Feil syndrome, cervical spina bifida, and other facial and limb abnormalities.
Orbital blowout fracture: Diplopia immediately after suffering a blowout fracture is common; 20% of patients will have persistent diplopia if no surgical intervention is performed. Infraorbital nerve hyperesthesia can be present after blowout fractures of the globe, although symptoms typically improve with time. Enophthalmos greater than 3 mm occurs in approximately 20% patients.
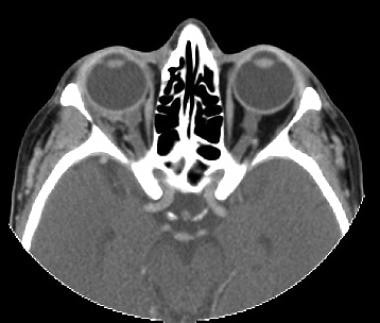
 Patient presented with persistent diplopia after an interpersonal altercation. Forced ductions revealed tight inferior and medial rectus muscles on right side. CT scan revealed orbital floor and medial wall fractures in right orbit.
Patient presented with persistent diplopia after an interpersonal altercation. Forced ductions revealed tight inferior and medial rectus muscles on right side. CT scan revealed orbital floor and medial wall fractures in right orbit.
Orbital metastases: Strabismus with diplopia is the most common finding in orbital metastases. Approximately 74% of patients present with a known primary tumor, in the remaining 26% no primary tumor is ever found despite thorough evaluation in 50% of cases. From the time of diagnosis of orbital metastasis, mean survival time is 13 months. Survival time after diagnosis is longer in breast carcinoma compared with prostate and lung carcinoma.
Sex
Duane retraction syndrome is slightly more common in females (54%) than in males (46%). [2]
Men are more than twice as likely to experience orbital trauma than women from most causes. The exceptions are domestic violence and sexual assault; almost all cases of orbital fractures in these situations occur in women.
Incidence of orbital metastasis from all tumor types is equal between men and women. Although men can develop breast carcinoma, there are no reports of orbital metastases of breast cancer in men.
Age
Duane retraction syndrome is a congenital condition. However, diagnosis often is delayed because of difficulty of eliciting full range of eye movements in infants.
Orbital trauma from almost all causes typically occurs in children and young adults.
Average age at the time of diagnosis of orbital metastases for breast and lung carcinoma is approximately 60 years.
Average age at the time of diagnosis of metastatic prostate carcinoma is 70 years.
Silent sinus syndrome can occur at any age.
Prognosis
The prognosis depends on the etiology.
Patient Education
Patients should be informed of the differential diagnoses and treatment plan.
Treatment should be directed at the underlying etiology.
-
Patient presented with persistent diplopia after an interpersonal altercation. Forced ductions revealed tight inferior and medial rectus muscles on right side. CT scan revealed orbital floor and medial wall fractures in right orbit.
-
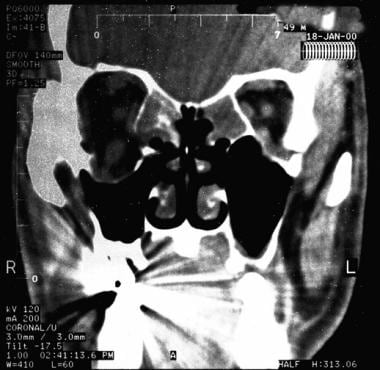
Patient with metastatic breast carcinoma to the intraconal space of the right orbit resulting in mild globe retraction and enophthalmos.