Background
The cornea [1] plays a crucial and vital role in the visual pathway. To maximize the visual potential of the eye, both the clarity of the cornea and the refractive power (curvature) are important. Any disturbance to the clarity or thickness of the cornea will affect its visual potential. The Descemet membrane and endothelial cells play a critical role.
Pathophysiology
The cornea is composed of 5 discrete anatomical components, each with specific functions to achieve the goal of clarity and refractive potential. The outermost component, the epithelium, provides a smooth surface due to the interactions of cytoskeletal components and tear film matrix. It also serves an important protective barrier function. The Bowman layer [2] or membrane, the second layer moving in toward the eye, serves as the smooth adhesion layer for the basement membrane of the epithelial cells. This layer is not crucial for clarity or visual function since removal of the Bowman layer during photorefractive keratectomy does not negatively affect vision.
The corneal stroma makes up the majority of the width of the cornea. It is composed of collagen fibrils arranged in a regular pattern to allow light to enter and pass through without being diffracted or reflected. Inflammation manifesting as stromal infiltrates and/or stromal edema results in the interruption of the regular periodicity of the collagen matrix and decreased corneal clarity. Because the cornea is avascular, nutrients and wastes are delivered and deposited anteriorly via the tear film and external environment, internally via corneal nerves, and posteriorly via the aqueous humor.
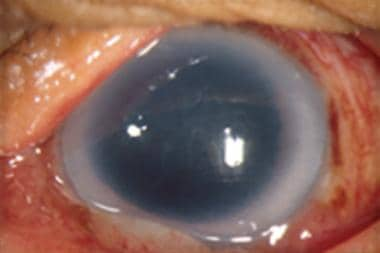
The innermost layer of the cornea is the endothelial cell layer, a monolayer of polarized cells. They are arranged with their apical portion toward the aqueous humor in the anterior chamber. The endothelial cells are responsible for maintaining the desiccation of the stroma by actively removing water. The Descemet membrane is the specialized basement membrane of the endothelial cells positioned between the stroma and the endothelial cell layer. Any condition that causes inflammation of the cornea or the anterior chamber can cause Descemet membrane folds.
Epidemiology
Frequency
United States
Descemet membrane folds is common because it is associated with many inflammatory conditions of the eye.
International
The frequency is similar to that in the United States.
Mortality/Morbidity
Morbidity due to decreased vision and pain exists.
Race
No predisposition to race exists.
Sex
Descemet membrane folds affects women and men equally.
Age
Descemet membrane folds affects all age groups with slower resolution of the folds in elderly persons.
-
Descemet membrane folds after surgery.
-
Diffuse illumination showing Descemet membrane folds after surgery.