Practice Essentials
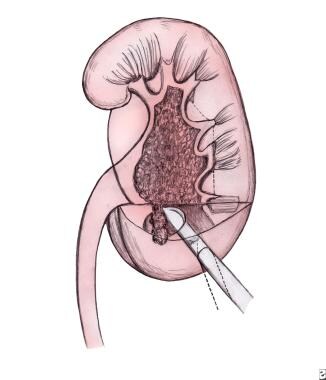
Nephrostomy is a term used to describe a passageway maintained by a tube, stent, or catheter that perforates the skin, passes through the body wall and renal parenchyma, and terminates in the renal pelvis or a calyx. [1] See the image below.
The nephrostomy has multiple functions but is used most frequently to provide urinary drainage when the ureter is obstructed and retrograde access is inadvisable or impossible. A nephrostomy can also be used to gain access to the upper urinary tract for various antegrade endourologic procedures, such as intracorporeal lithotripsy, chemical stone dissolution, antegrade radiologic studies of the ureter, and double-J stent placement.
Nephrostomy has several other functions, including the following:
-
To remove or dissolve renal calculi
-
To obtain direct access to the upper urinary tract for various endourologic procedures
-
To diagnose ureteral obstruction, filling defects, and anomalies via antegrade radiography
-
To deliver chemotherapeutic agents to the renal collecting system
-
To provide prophylaxis after resection for local chemotherapy in patients with tumors of the renal pelvis
An assessment of blood serum creatinine can be used to help evaluate obstruction and dilatation of the renal pelvis. Elevated levels indicate that the renal pelvis obstruction is related to kidney function. However, in all patients, nephrotoxic substances should be excluded as a source of renal failure. A renal scan is helpful in borderline cases (ie, when the renal pelvis is normal or minimally dilated and the creatinine level is slightly elevated).
To determine whether an obstruction is new or old, the patient's history is essential. Old radiographs or sonograms can also be helpful. Most commonly, acute obstruction is caused by renal stones, whereas chronic obstruction is caused by renal or ureteral tumors and postoperative and radiation strictures of the ureter. A prior instance of renal failure was usually due to chronic obstruction.
The most dangerous cases of renal obstruction occur in patients who have urosepsis with renal obstruction and elevated creatinine levels. Fast renal access can be lifesaving in these patients. However, as with any procedure, the patient's general situation and prognosis must be evaluated prior to the procedure.
Tumors, such as sarcomas, ovarian tumors, and other retroperitoneal tumors (Ormond disease, intraperitoneal tumors), can compress the ureter. A nephrostomy may be required in all of these cases. Do not attempt retrograde access if a tumor spill or vascular lesion is likely to develop. Depending on the anatomical situation of the stricture, patients with ureteral strictures after vascular surgery, eg, for an aortofemoral bypass, should undergo nephrostomy placement.
Anatomical anomalies, such as ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction, can create difficulty in retrograde access. Tumors or strictures that completely compress the ureter complicate or prevent retrograde access to the kidney. Passing a stent or guidewire antegrade rather than retrograde can be easier, as cystoscopy is not needed for antegrade access to the ureter.
Flexible antegrade pyeloureteroscopy can be performed through the nephrostomy when retrograde access to the ureter or kidney is not possible because of anatomic anomalies, tumors, or strictures.
History of the Procedure
In 1912, Hugh Hampton Young passed a pediatric cystoscope percutaneously into a massively hydronephrotic kidney. Willard Goodwin, MD, described percutaneous access and nephrostomies in 1955. [2] In 1976, Fernström and Johansson performed a percutaneous nephrostomy specifically to remove a kidney stone. [3] In 1979, Smith and colleagues, from the University of Minnesota, began to remove stones in the renal pelvis and the ureter through percutaneous nephrostomy tracts. Nephrostomy tube placement is shown in the image below. In 1981, Alken and colleagues, who were working in Germany, removed stones through matured percutaneous tracts. [4]
Problem
Nephrostomy involves creating an opening into the kidney to maintain temporary or permanent urinary drainage. The collecting system of the kidney is punctured percutaneously with a needle under fluoroscopic, ultrasonographic, or CT guidance. The needle is passed through the skin, subcutaneous tissue, external and internal muscle layers, and the renal parenchyma to reach the collecting system. When the needle has entered the renal collecting system, a guidewire is passed through the needle into the kidney and possibly down the ureter. Over the guidewire, various dilators can be used to establish and enlarge the nephrostomy tract, which is then maintained by a tube.
Alternatively, a nephrostomy tube can be placed during open surgery. In this procedure, a tube is placed into the renal pelvis, perforating the renal parenchyma and puncturing the flank musculature, subcutaneous tissues, and skin to create a direct passage between the renal collecting system and the external environment.
Anesthetic agents can be more hazardous in patients with overt renal shock. Therefore, performing the nephrostomy under local anesthesia is especially important when the procedure is potentially lifesaving.
Presentation
Symptoms of upper urinary tract obstruction can include flank or abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, or mild-to-severe urosepsis, including septic shock. Patients with calculi may be asymptomatic.
Indications
Percutaneous nephrostomy is occasionally essential, if not lifesaving, in the treatment of acute or chronic upper urinary tract obstruction. It is the first step in obtaining antegrade access to the kidney for various procedures. Specific indications for percutaneous nephrostomy include the following:
-
Acute or chronic upper urinary tract obstruction in which access to the kidney is impossible from the lower urinary tract because of stones, infections, tumors, or anatomic anomalies, especially when a double-J stent cannot be placed through the ureter because of above-mentioned circumstances
-
When a patient's creatinine level is rising above the reference range and the urine cannot be drained through the ureter
-
Renal pelvis disorders (eg, UPJ obstruction, horseshoe kidneys, ureter duplex, ureter fissures, double renal collecting systems)
-
Hydronephrosis in renal transplant allografts: When dilatation of the renal pelvis affects kidney function to the extent that double-J stent placement is difficult or impossible, percutaneous nephrostomy may be an easier option.
-
Treatment of staghorn calculi and large or lower-pole kidney stones (when a percutaneous nephrolithotomy [PCN] is likely to be followed because of the stone burden and an extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy [ESWL] is less likely to be successful)
-
Contraindications to ESWL (ie, size of patient): Most ESWL units have a weight limit of 140 kg (approximately 300 lb).
-
Body habitus that prevents ESWL (eg, contractures): Disabled patients occasionally cannot be positioned on an ESWL unit in a prone or supine position.
-
Stones or tumors associated with distal obstruction or a foreign body that cannot be removed through the ureter
-
When rapid dilation of the nephrostomy tract is required (eg, when access is needed instantly for operative procedures within the renal collecting system [for stone removal or tumor ablation])
-
Prolonged sequential dilatation: Gradually increasing the catheter size may be necessary when a nephrostomy tube is placed permanently for urine drainage in patients in whom a retrograde access to the kidney is impossible (eg, advanced metastatic tumors, loss of the total ureter, patients with a palliative nephrostomy tube whose cases are inoperable).
-
A rare indication is antegrade nephrostomy to control a ureteral lesion after ureteral trauma that cannot be fixed in a retrograde fashion in a nonobstructed kidney. This can occur with a completely dissected ureter after gynecological, surgical, or urological procedures discovered after the procedure. Most likely, a urinoma has developed around the dissected ureter, with the kidney itself not being obstructed but in being need for a nephrostomy.
-
In an emergency situation a nephrostomy may always be mandatory.
-
In a study by Cyphers et al, the most common indication for percutaneous nephrostomy in neonates and young infants was ureteropelvic junction obstruction [5]
Relevant Anatomy
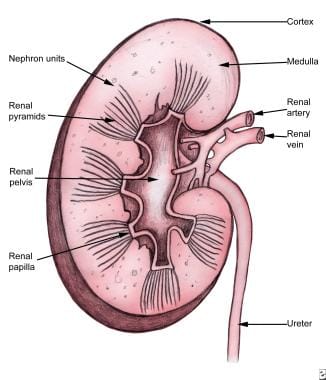
The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs below the diaphragm—below the liver on the right and below the spleen on the left. The kidney is located at the level of the 10th to the 12th ribs. The principal areas of the kidney include the renal cortex and medulla, renal pelvis, renal papillae, renal pyramids, ureter, renal artery, and renal vein. Renal anatomy is shown below.
A fat capsule, the Gerota fascia, surrounds the kidney. The Brödel line also has historical interest. The minor renal calyces come together to the major renal calyces and make up the renal pelvis. The following organs supply blood to the kidney, in descending order: renal artery, interlobar artery, arcuate artery, intralobular artery, afferent arterioles, and glomerulus. All arterioles end arteries without communication, which is important for a possible embolization.
Contraindications
Contraindications for nephrostomy include the following:
-
Bleeding diathesis (eg, hemophilia, thrombocytopenia)
-
Uncontrolled hypertension [6]
-
Anticoagulant use (eg, aspirin [relative contraindication], heparin, warfarin)
-
Renal anatomy.
-
Positioning of nephrostomy tube into the lower pole of the kidney.
-
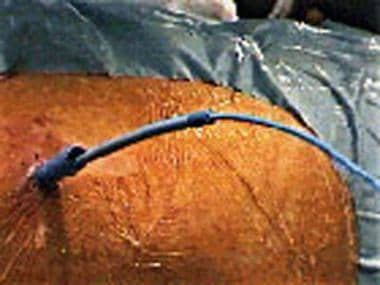
Outside appearance of a nephrostomy tube from the flank after stone removal.
-
CT scan of bilateral hydronephrotic kidneys without intravenous contrast medium.
-
CT scan with dilated right ureter without intravenous contrast medium.