Practice Essentials
The term dermoid cyst does not appear to be restricted to a single kind of lesion nor is it used in only a single medical discipline. The term dermoid cyst can be found in the vocabulary of dermatologists, dermatopathologists, general pathologists, gynecologists, neurosurgeons, or pediatricians. If asked, all of these clinicians would most probably define and describe dermoid cysts differently. For example, gynecologists and general pathologists might say that a dermoid cyst is a cystic tumor of the ovary. In contrast, neurosurgeons tend to view a dermoid cyst is associated with a congenital cyst of the spine or an intracranial congenital cyst. For pediatricians and dermatologists, dermoid cyst means subcutaneous cysts, which are usually congenital. [1]
In all disciplines, however, the common factor is the presence of a solitary, or occasionally multiple, hamartomatous tumor. The tumor is covered by a thick dermislike wall that contains multiple sebaceous glands and almost all skin adnexa. Hairs and large amounts of fatty masses cover poorly to fully differentiated structures derived from the ectoderm.
Depending on the location of the lesion, dermoid cysts may contain substances such as nails and dental, cartilagelike, and bonelike structures. If limited to the skin or subcutaneous tissue, dermoid cysts are thin-walled tumors that contain different amounts of fatty masses; occasionally, they contain horny masses and hairs.
See the image below.
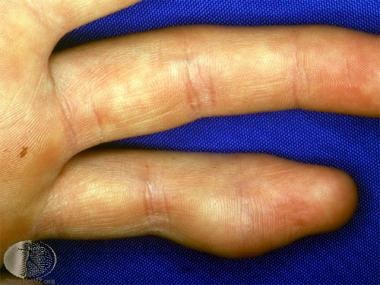 Dermoid cyst in an unusual location. Courtesy of DermNet New Zealand (http://www.dermnetnz.org/assets/Uploads/lesions/d-cyst.jpg).
Dermoid cyst in an unusual location. Courtesy of DermNet New Zealand (http://www.dermnetnz.org/assets/Uploads/lesions/d-cyst.jpg).
Also see orbital dermoid and limbal dermoid.
Pathophysiology
Dermoid cysts in the skin and subcutis occur mostly on the face, neck, or scalp.
In addition to the skin, dermoid cysts can be intracranial, intraspinal, or perispinal. Intra-abdominal cysts, such as cystic tumors of the ovary or omentum, occur as well.
Etiology
Dermoid cysts are true hamartomas. Dermoid cysts occur when skin and skin structures become trapped during fetal development.
Histogenetically, dermoid cysts are a result of the sequestration of skin along the lines of embryonic closure.
Workup
Radiography, CT scanning, and MRI are helpful in making the correct differential diagnosis of dermoid cysts. MRI is particularly helpful in diagnosing intracranial or intramedullary dermoid cysts and in assessing the dissemination of fatty masses or droplets. MRI is helpful in planning surgical procedures and in assessing therapeutic success. Three-dimensional reconstructed assessment of a nasal dermoid cyst also may be of value, especially when focusing on the intracranial connection. [2] An ultrasound algorithm to differentiate thyroglossal duct and dermoid cysts has been proposed. [3]
See Histologic Findings.
Treatment
See Surgical Care.
Epidemiology
No information is available about the prevalence of dermoid cysts. In gynecology, the literature describes dermoid cysts as relatively rare tumors, a cystic teratoma that most often occurs in individuals aged 15-40 years. In neurosurgery, dermoid cysts are rare. In dermatology and pediatrics, dermoid cysts are relatively uncommon.
Of the 2639 eyelid tumors from a Chinese study, the 5 most common eyelid benign ones were inflammatory lesions, melanocytic nevi, papillomas, dermoid cysts and epidermoid cysts, and epithelial cysts. [4]
No racial predilection is apparent; however, most cases of dermoid cysts in the literature are described in White persons.
Dermoid cysts of the ovary are sex restricted, that is, they occur only in the female population. In other dermoid cysts, no sex predilection has been found.
Age
Dermoid cysts have been described in persons of all ages.
Dermoid cysts on the face, neck, or scalp are subcutaneous cysts that are usually present at birth. Intracranial or perispinal dermoid cysts are most often found in infants, children, or young adolescents.
Intra-abdominal dermoid cysts are described in females aged 15-40 years. For example, cystic teratoma is a relatively rare tumor that most often occurs in females aged 15-40 years.
Most dermoid cysts on the floor of the mouth occur in individuals aged 10-30 years. There are few descriptions of oral dermoid cysts in newborns or children.
Prognosis
If dermoid cysts are diagnosed early and treated with complete surgical excision, the prognosis is good, and no further complications are expected.
In patients with carcinomatous transformation, the prognosis depends on the stage of the malignant disease (locally limited or spreading) and the success of therapy.
Although dermoid cysts are located in connection with the spinal channel (as described in neurosurgery literature), no deaths are directly linked to ruptures of the cyst or to the spreading of fatty and occasionally, infected masses in subarachnoid, ventricular, or subdural compartments. However, rupture or spread can lead to severe neurologic complications such as secondary spinal subdural abscesses.
-
Dermoid cyst in an unusual location. Courtesy of DermNet New Zealand (http://www.dermnetnz.org/assets/Uploads/lesions/d-cyst.jpg).




