Background
Tumor of the follicular infundibulum is a rare benign adnexal tumor arising from the follicular infundibulum. The histopathology of the tumor is distinctive, which occurs as a platelike dermal nodule with multiple thin connections to the overlying epidermis (see the images below). [1] The tumor usually manifests as a single lesion, but an eruptive (multiple) form may occur.
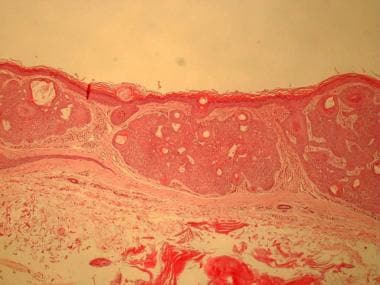 Tumor of the follicular infundibulum shows a platelike dermal tumor with anastomosing islands and cords with connections to the overlying epidermis and horn cysts (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 40X magnification).
Tumor of the follicular infundibulum shows a platelike dermal tumor with anastomosing islands and cords with connections to the overlying epidermis and horn cysts (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 40X magnification).
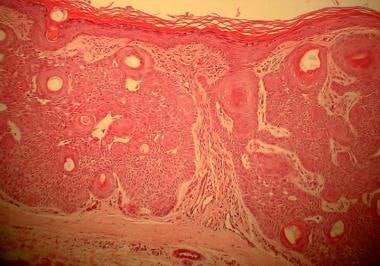 Tumor of the follicular infundibulum shows epidermal connections, horn cysts, and anastomosing islands (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 100X magnification).
Tumor of the follicular infundibulum shows epidermal connections, horn cysts, and anastomosing islands (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 100X magnification).
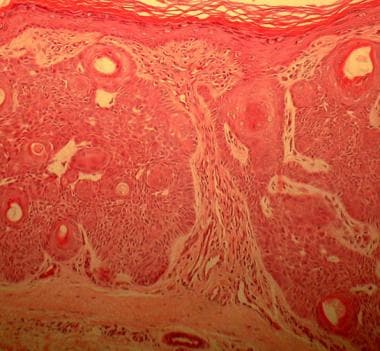 Tumor of the follicular infundibulum shows epidermal connections, peripheral palisading, and horn cyst (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400X magnification).
Tumor of the follicular infundibulum shows epidermal connections, peripheral palisading, and horn cyst (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400X magnification).
Pathophysiology
The cause of follicular infundibulum tumor is unknown. Follicular infundibulum tumor is a benign tumoral proliferation that arises from the follicular infundibulum. The external root sheath of the follicle has been shown to give rise to these tumors. A possible relation to sun exposure has been reported.
Epidemiology
Frequency
Follicular infundibulum tumor is uncommon. Since the original report from Mehregan and Butler in 1961, only a few new cases have been reported. [2] The overall relative frequency ranges from 3-10 cases per 100,000 specimens examined.
Race
No racial predilection is known for follicular infundibulum tumor.
Sex
A slight female predominance is recognized for follicular infundibulum tumor. [3]
Age
Most cases of follicular infundibulum tumor occur in patients older than 60 years.
Prognosis
Prognosis is excellent in follicular infundibulum tumors. Follicular infundibulum tumor is benign, although malignant transformation to a basal cell carcinoma was reported twice in a patient with multiple lesions. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma have also described within a field of multiple infundibulomas. [4]
Additional case studies, both reported in 2009, have proposed conflicting views of the nature of follicular infundibulum tumor. First, Abbas and Mahalingam suggest that tumor of the follicular infundibulum is a benign epidermal reaction pattern. In their series of 74 cases, all showed benign histologic features, and, in addition, 25% were identified in association with other cutaneous lesions, which included basal cell carcinoma, actinic keratosis, desmoplastic melanoma, junctional nevus, tricholemmoma, and epidermoid cyst. [5]
Second, in the same journal, Weyers et al made the statement that tumor of the follicular infundibulum is basal cell carcinoma. In their series of 24 cases, they noted, often only focally, changes typical of basal cell carcinoma such as peripheral palisading, germinative cells, crowding of cells, individual necrotic neoplastic cells, fibromucinous stroma, and stromal-epithelial island clefts. In addition, 5 cases were associated with obvious basal cell carcinoma, and, in some cases, recurrences were noted in completely removed basal cell carcinoma in which tumor infundibulum was present at the surgical margins. [6]
-
Tumor of the follicular infundibulum shows a platelike dermal tumor with anastomosing islands and cords with connections to the overlying epidermis and horn cysts (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 40X magnification).
-
Tumor of the follicular infundibulum shows epidermal connections, horn cysts, and anastomosing islands (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 100X magnification).
-
Tumor of the follicular infundibulum shows epidermal connections, peripheral palisading, and horn cyst (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400X magnification).





